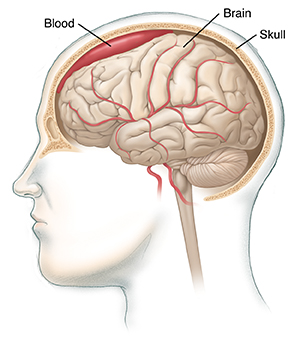
Craniotomy is a surgical opening made in the skull for treatment of several types of problems in or around the brain. Special tools are used to remove a piece of the skull and allow access to the brain or areas surrounding the brain for surgical treatment. The problems discussed below are the most common reasons for doing a craniotomy.
Brain injury
A brain injury can result from a direct blow to the head or even whiplash. It can cause injury, bleeding, and swelling of the brain. It can also cause bleeding around the brain. The treatment goal is to stop any bleeding and reduce pressure inside the skull. Blood and damaged tissue may be removed. When the brain swells too much, the piece of bone might not be placed back for a few weeks.
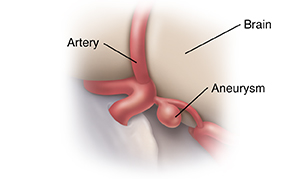
Aneurysm
An aneurysm is a balloon-like defect in an artery wall. Over time, the defect bulges and weakens. This allows blood to leak out. The leaking blood causes a sudden headache and can damage the brain. The treatment goal is to control damage and prevent future bleeding. This is done by placing a clip on the neck of the aneurysm or coil, depending on the size of the aneurysm.
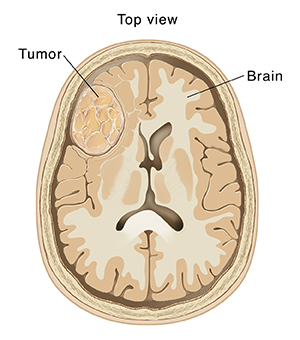
Brain tumor
A tumor is a mass of abnormal cells. A primary brain tumor starts in the brain. Some tumors start in the tissues around the brain and push on the brain or invade the brain. A metastatic brain tumor grows from cells that spread to the brain from some other site in the body. The goal is to take a tissue sample (biopsy) to find out the type of tumor and to remove as much of the tumor as safely as possible. Depending on the tumor, other treatments may also be needed.
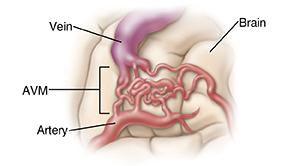
Arteriovenous malformation
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is abnormal snarled tangles of blood vessels that cause irregular connections between arteries and veins. An AVM can prevent normal blood flow through part of the brain. This keeps the brain from getting oxygen. AVMs can bleed into brain tissue. The treatment goal is to stop blood flow within the AVM, channel it along the normal route, and save the brain tissue.
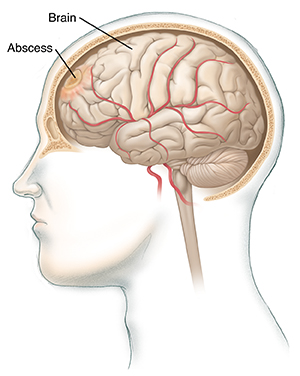
Brain abscess
An abscess in the brain is an infection that forms a mass. A brain abscess is always treated with antibiotics. In some cases, it's also treated with surgery.