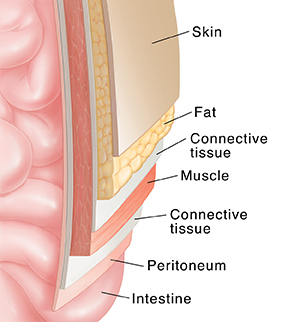
The belly (abdomen) is the largest space (cavity) in the body. It lies between the chest and the pelvis, holding many of the body’s organs. These include the liver, stomach, and intestines.
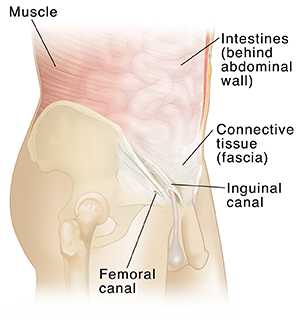
The groin is the area in the body where the upper thighs meet the lowest part of the abdomen. Normally, the abdomen and groin are kept separate by a wall of muscle and tissue. The only openings in the wall are small tunnels called the inguinal and femoral canals. These allow nerves, blood vessels, and other structures to pass between these 2 areas.
The abdomen and groin
-
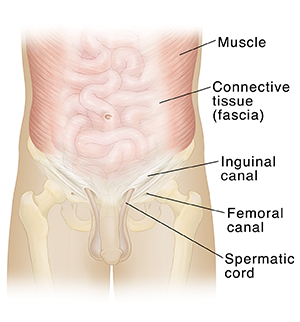
Muscles. These are soft tissues. They enclose the intestines and other organs in the abdomen.
-
Connective tissue. These help bind the muscles together.
-
Inguinal canal. This tunnel in the groin is formed by layers of muscle and other tissues in the wall of the abdomen.
-
Femoral canal. This tunnel in the wall of the abdomen allows blood vessels and nerves to pass through the groin into the leg.
-
Spermatic cord. This passes through the inguinal canal and connects to the testicle.