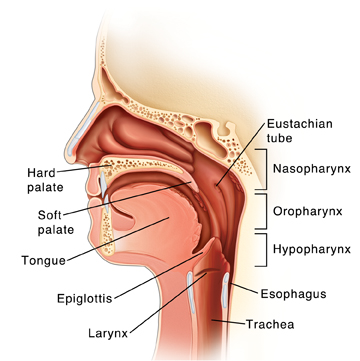
Hard palate. This separates the nose from the mouth.
Soft palate. The back of the roof of the mouth.
Epiglottis. This keeps food and liquids out of the trachea when you swallow.
Larynx (voice box). This makes sound used for speaking.
Eustachian tube. The tube that connects the throat to the ear.
Nasopharynx. The area at the top of the throat behind the nose.
Oropharynx. The area at the middle of the throat behind the mouth.
Hypopharynx. The area at the lower part of the throat.
Esophagus. The tube that carries food and liquids from the throat to the stomach.
Trachea. The tube that carries air between the throat and the lungs.
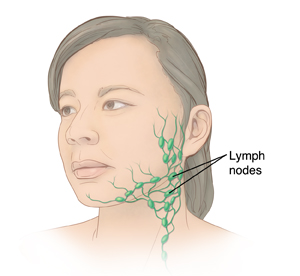
Lymph nodes. Bean-shaped organs that help the body fight infections.