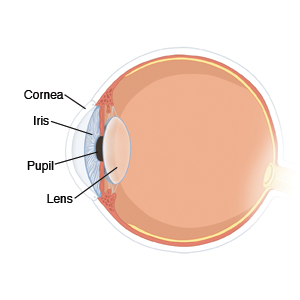
The iris is the colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil. Iritis is an inflammation of the iris. It can be caused by injury to the eye or disease elsewhere in the body. Diseases linked to iritis include Lyme disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and rheumatoid arthritis. Often, no cause is found.
Iritis usually develops suddenly in one eye. Symptoms include redness, pain in the eye or brow area, sensitivity to light, and blurred vision.
Iritis is treated with eye drops to dilate the pupil and reduce pain. This will cause your vision to be blurred from a few hours up to a week, depending on the medicine used. Steroid drops are also prescribed to reduce pain from inflammation. Iritis from eye injury usually resolves in 1 to 2 weeks. Iritis from other causes may take several weeks to months to resolve.
Home care
-
Use eye drops as prescribed.
-
Wear sunglasses to decrease light sensitivity and discomfort.
-
If your eye is dilated or if you have been given an eye patch, your driving ability will be affected. Don't drive until the blurred vision wears off and you no longer need an eye patch.
-
You may use acetaminophen or ibuprofen to control pain, unless another medicine was prescribed. Talk with your healthcare provider before taking these medicines if you have chronic liver or kidney disease, or if you have ever had a stomach ulcer or digestive bleeding.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider, or as advised.
When to get medical advice
Contact your healthcare provider right away if any of the following occur:
-
Symptoms don’t start to improve after 1 week
-
Iritis from eye injury causes symptoms for more than 2 weeks
-
Pain increases
-
You lose some or all of your vision