Dizziness and fainting can have many different causes. The information below describes some examples of possible causes your healthcare provider will look to rule out.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
BPPV results when calcium carbonate crystals inside the inner ear shift into the wrong position. BPPV causes episodes of vertigo, a spinning sensation, nausea, and vomiting. Episodes most often happen when you move your head in a certain way. This is more common in people age 65 and older.
Infection or inflammation
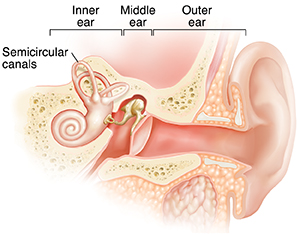
The semicircular canals of the inner ear are 3 tiny tubes that loop in 3 different directions. As fluid moves in the tubes, signals are sent to the brain that help you maintain balance. These semicircular canals may become infected or inflamed. In this case, they can send the wrong balance signals. This can cause vertigo.
Ménière disease
Ménière disease happens when there is too much fluid in the semicircular canals. This can cause vertigo. It also can cause hearing problems and buzzing or ringing in the ears (called tinnitus). You may also have a feeling of pressure or fullness in the ear.
Syncope
Syncope is fainting that happens when the brain doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood. It can be caused by low heart rate or low blood pressure. It is called vasovagal syncope if this occurs as part of a fear or anxiety response. It can also be caused by sitting or standing up too quickly. This is called orthostatic hypotension. Syncope may also be due to a heart valve problem, an abnormal heart rhythm, or other problems with your heart, lungs, or blood vessels.
Other causes
Other causes include:
-
Problems with the brain. These include a stroke or bleeding (hemorrhage) in the brain. You may need certain tests to rule out these conditions.
-
Medicines. Certain medicines can cause dizziness and even fainting. In some cases, stopping a medicine too quickly can lead to withdrawal symptoms. These include dizziness and fainting.
-
Anxiety. Being anxious can lead to breathing changes, such as hyperventilation. These can lead to dizziness and fainting.
Other causes of dizziness and fainting also exist. Talk with your healthcare provider for more information.