Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a group of conditions that cause inflammation and scarring around the tiny air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. The changes make it hard to take in oxygen. People with ILD may feel short of breath and tired. They may also have a dry cough and chest discomfort.
Examples of ILD include these conditions:
-
Asbestosis
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
-
Sarcoidosis
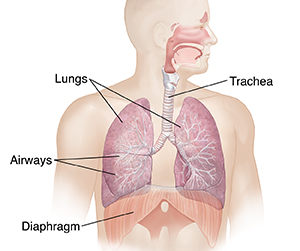
Inside your lungs
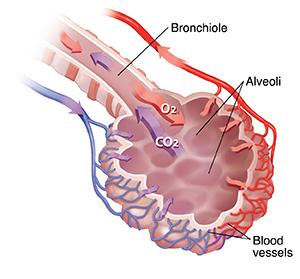
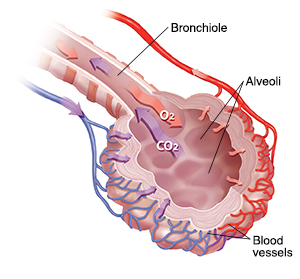
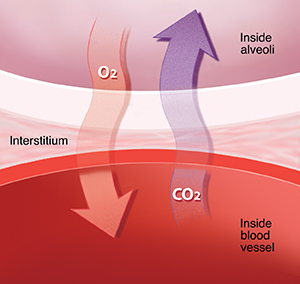
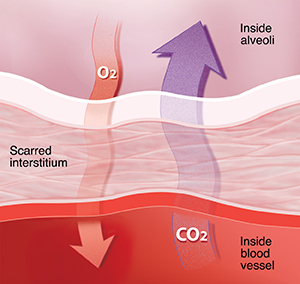
When you breathe, air travels in and out of your lungs through the windpipe (trachea), airways (bronchi), and branching airways (bronchioles). Oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are exchanged in the tiny air sacs (alveoli). Oxygen passes from the alveoli to the blood vessels through the tissue called interstitium. The blood vessels then carry oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body. Carbon dioxide moves back from the blood vessels to the alveoli. You then breathe it out.
How lungs become damaged
With ILD, the lungs have inflammation and scarring around the alveoli. The changes make it hard to take in oxygen.
Causes of ILD
In most cases, ILD has no known cause. This is called idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Some known causes of ILD include:
-
Dust from asbestos or silica, coal dust, gases, fumes, or poisons
-
Some medicines
-
Radiation therapy
-
Certain lung infections
-
Connective tissue disease, such as scleroderma, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis
-
Smoking. Smoking can cause ILD or make it much worse.
Treatment and healthcare providers for ILD
Treatment may include:
-
Medicine
-
Breathing methods
-
Exercise
-
Pulmonary rehab
-
Supplemental oxygen
-
Smoking cessation programs
-
In some cases, you may need a lung transplant
Your healthcare team may include:
-
Primary care provider. This could be your family healthcare provider or internist.
-
Pulmonologist. This is a healthcare provider who specializes in treating lung problems.
-
Respiratory therapist. This person gives treatment and support for people with lung disease.
-
Social worker. This person helps with your daily needs and family life, accessing community resources, counseling services, and stress management.