Total knee replacement is a type of surgery to replace a damaged knee joint. Minimally invasive surgery uses two or more small cuts (incisions) instead of a single large incision. The methods to expose the knee joint are also less invasive than traditional knee replacement surgery. The procedure is done by an orthopedic surgeon. This is a doctor with special training in treating bone, joint, and muscle problems. Not everyone is a candidate for this type of surgery.
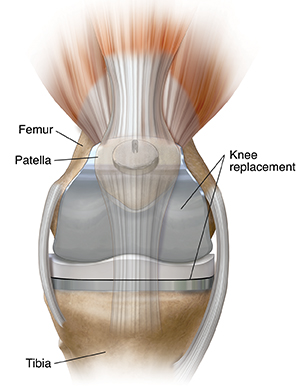
About the bones of the knee
The knee joint is made of:
-
The lower end of the thighbone (femur).
-
The upper part of the shinbone (tibia).
-
The kneecap (patella).
Normally these bones move smoothly against each other. If there is joint damage, the spongy cushion (cartilage) that lines the joint wears away. The bones no longer move smoothly against each other. This causes pain. During a total knee replacement, parts of the bone that make up the knee joint are removed. They are replaced with metal and plastic parts to create a new joint.
Why minimally invasive total knee replacement is done
You may need this surgery if you have severe damage to your knee joint. This can cause pain and interfere with your daily activities. Conditions that may damage this joint include:
-
Osteoarthritis. Also called wear-and-tear arthritis. The cartilage wears away as a person ages. This is the most common cause of damage.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis. This is a type of arthritis that affects not only joints, but the whole body. Serious joint damage may occur if it’s not treated.
-
Osteonecrosis. This is damage caused by decreased blood supply to a bone.
-
Injury. This may be a break (fracture).
-
Tumor. This is an abnormal growth of the bone. It may or may not be cancer.
Total knee replacement may help reduce your pain, make it easier to move your knee, and improve your quality of life. Knee replacement is most often only advised if other treatments haven’t worked.
How minimally invasive total knee replacement is done
The surgery is done by an orthopedic surgeon. This is a doctor who specializes in treating bone, muscle, joint, and tendon problems. The surgery can be done in several ways. The surgeon makes a cut (incision) through the skin and muscles near the knee. They remove the damaged portions of your thigh and shin bones. The surgeon also removes a small amount of healthy bone under the damaged bone. They put metal implants into the joint space. They are usually cemented to the remaining bone. The surgeon may also remove part of the underside of the kneecap. They put a plastic spacer between the metal implants. This will let you to move your knee more easily.
Risks of minimally invasive total knee replacement
All surgeries have some risks. The risks of this surgery include:
-
Infection.
-
Bleeding.
-
Blood clots.
-
Injury to nerves.
-
Loosening of the knee joint.
-
Limited knee movement.
-
Continued knee pain.
-
Problems from anesthesia.
Your risks vary based on your age and general health. For example, if you are a smoker or if you have low bone density, you may have a higher risk of certain problems. People with diabetes may also have a higher risk for problems. Ask your doctor which risks apply to you.