External bleeding occurs when the body’s protective skin is broken. In severe cases, blood loss may place the person’s life in danger. Direct pressure usually stops bleeding, even the rush of blood from an artery.
When to call 911
Call
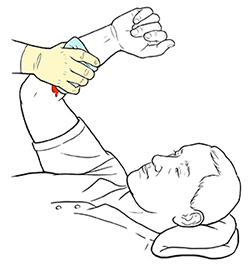
Apply direct pressure
-
Put on gloves or use other protection to prevent contact with the person’s blood.
-
Press directly on the wound with a clean gauze patch or cloth.
-
Keep the pressure constant for at least 5 minutes. This allows the blood to thicken (clot), preventing more bleeding.
-
Don't lift the bandage to check on the bleeding until at least 5 minutes have passed.
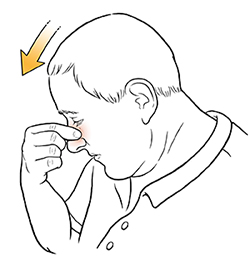
Pinch off nosebleeds
Reassure the person with the nosebleed and tell them to do the following:
-
Pinch their nostrils below the bone.
-
Tip their head slightly forward and sit quietly. Maintain pressure on the nose for at least 5 minutes.
-
Don't tilt their head backward. Tilting back may cause blood to run backward into their mouth and throat.
-
Don't destroy the clot by blowing or rubbing the nose after the bleeding stops.
Bleeding: How much is too much?
The person’s age, body size, and overall health all help determine when bleeding becomes serious. Concentrate on the person’s condition and appearance—not on the amount of blood lost. Bleeding from head wounds and nose bleeds can be dramatic while still being safe. Watch the person for signs of shock. If any shock symptoms appear, blood loss is a threat to life.
Symptoms of shock include:
-
Pale, clammy skin.
-
A racing pulse.
-
Confusion or unconsciousness.
-
Pulsing, spurting bleeding that can't be stopped with direct pressure.