Carotid endarterectomy is a surgery to remove plaque from the carotid artery and improve blood flow to the brain. This surgery has a low risk for stroke (2% to 3%) in those with no pre-surgery symptoms. It often has a quick recovery with little pain. You may be asleep under general anesthesia. Or you may be awake with sedation and local anesthesia to control pain. Your surgeon will discuss which is a better option for you before your surgery.
How the endarterectomy is done
-
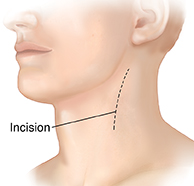
Make the skin incision. The surgeon makes a cut (incision) in the skin over the carotid artery in the neck.
-
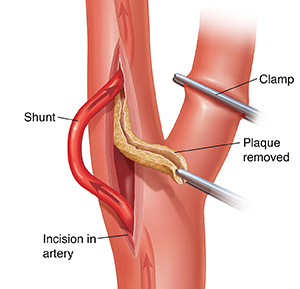
Open the artery. The surgeon places clamps on the artery above and below the blockage. This temporarily stops blood flow. The brain receives blood from the carotid artery on the other side of your neck. The surgeon then makes an incision in the artery itself.
-
Place the shunt. A shunt may be used to preserve blood flow to the brain during the procedure. After the shunt is in place, the clamps are removed from the internal carotid artery. In some cases a shunt is not needed because the brain is receiving enough blood through the carotid artery on the other side of your neck.
-
Remove plaque. The surgeon loosens plaque from the artery wall. The plaque is then removed, often in a single piece. The surgeon looks at the artery to confirm that all of the plaque has been removed.
-
Close the incision. The surgeon closes the incision using either sutures or a patch. The clamps are then removed. Next, the skin incision is sutured closed. A tube or drain may be put in place to keep fluids from collecting around the area.
The surgery usually takes around 2 hours. But it may take longer depending on the anesthesia and your situation.